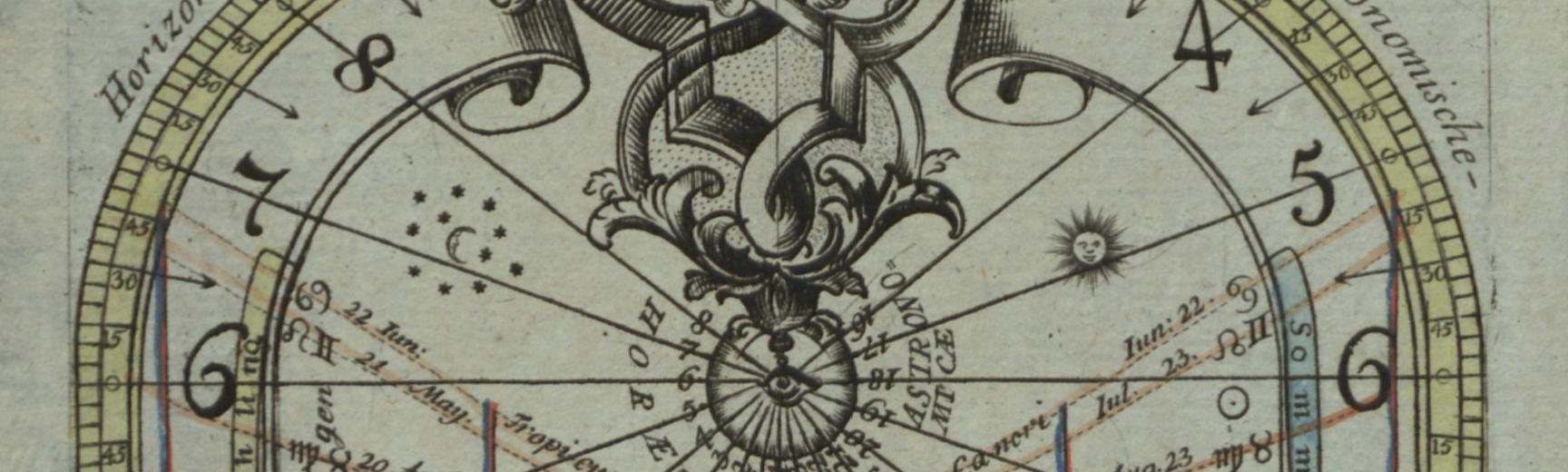
Paper instruments

Print (Engraving) Paper sundial with gnomon by Johan Conrad Gütle, Nuremberg, 17th Century.
Most of the classic mathematical instruments usually seen in brass, ivory and other materials – such as astrolabes, sundials, quadrants, nocturnals – can also be found made of paper. Three or four hundred years ago, paper instruments were more common than the impression given by our museum displays and catalogues. Their lower survival rate is only part of the reason. It is also because, where they do survive, it is often in books, among manuscripts, or within collections of prints.
Sometimes they may be hard to distinguish from mere illustrations, and indeed serve both functions. Apian’s Instrumentbuch (1533) illustrates the various dials and quadrants he describes, but customers could also buy from him the same woodcuts printed on separate sheets to cut out, mount on wood perhaps, and use as real instruments. Some instruments found in books are meant to be used in situ, such as the volvelles and other illustrations with moving parts that were a popular feature of astronomical books and manuscripts. Apian’s Astronomicum Caesareum is the most spectacular example.
It was not uncommon for a book about, for instance, the astrolabe, to contain an instrument. A good example in the Museum’s collection is the astrolabe by Krabbe (1583), because it exists in both forms.
The tradition dates from early times in manuscript (using paper, parchment or vellum). The Museum has a paper and parchment hand-drawn astrolabe dated 1492 (91897). Printing did not eclipse the tradition, nor the educational value, of designing or making one’s own instruments on paper; students and enthusiasts of geometrical studies were still making their own in the 18th century. The Lewis Evans collection of ‘dialling’ manuscripts of the 16th to 18th centuries not only shows the continuing importance to geometry studies of learning how to design and make sundials and similar instruments, but preserves many examples of instruments achieved in ink and paper.
Printing allowed multiple copies to be made from one original copper printing plate or woodblock, increasing the dissemination of instruments, and reducing the price. Students who could never have afforded (or whose rich parents would not have trusted them with) an expensive brass instrument instead purchased paper instruments from Georg Hartmann in 16th-century Nuremberg (49296), or from John Prujean in 17th-century Oxford (48821 and 52008).
The earliest printed paper instruments are those designed by Regiomontanus, who set up a joint instrument workshop and printing press in Nuremberg in the 1470s, soon after the invention of printing. Four instruments occur in his astronomical calendars (the Museum has the editions of 1476 and 1482, plus a greatly enlarged version issued by Stoeffler in 1518), which are both integral parts of the book and functioning instruments. Regiomontanus’s example was crucial, and his admirers in the next generation, like Stoeffler, Schoener, Hartmann, and Apian, took up the project in earnest. Printed paper instruments continued to be in wide use into the 19th century.
Some instruments, such as quadrants and cylinder sundials, were routinely made of printed paper, as of course were compass cards. Henry Sutton was one of the highly skilled 17th-century instrument makers whose trade included accurately engraved paper instruments (25257 and 60120). The tradition was continued in the following centuries by scientific teachers and popularisers such as James Ferguson (14117, 14163, and 33394) and Lewis Evans.